The human brain remains one of the last great frontiers of science, shrouded in complexity that can baffle even the most seasoned neuroscientists. The latest research, which meticulously examined a minuscule fragment of a mouse brain, has yielded staggering insights that could transform our understanding of neurological mechanisms. While the sample size may barely compare to the vast landscape of our mind, the dedication of over 150 researchers, spanning 22 institutions, speaks volumes about the effort to decode this enigmatic organ. This work not only charts the intricate connections among 84,000 neurons but also reveals the potential for future breakthroughs in understanding human cognition and mental disorders.
A Microscopic Odyssey
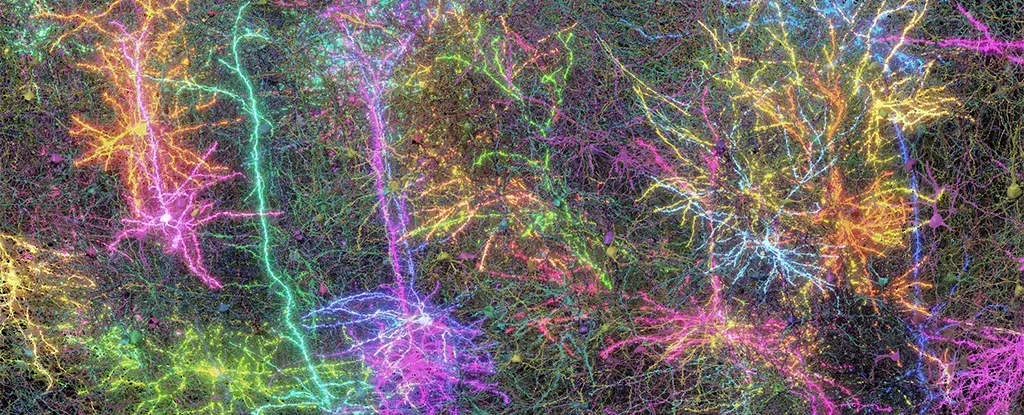
By focusing on an area smaller than a grain of sand, scientists managed to unveil over half a billion synaptic connections woven into 5.4 kilometers of neural pathways. This feat, culminating in the most detailed rendering of a mammalian brain to date, required nine painstaking years of dedicated labor, with roots planted in various leading institutions such as Princeton University and the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The process involved an unprecedented blend of sophisticated artificial intelligence tools and meticulous human analysis, showcasing our unique ability to unravel biological puzzles piece by piece.
Neuroscientist Andreas Tolias illustrates the sentiment behind this monumental achievement: “The brain is this biological tissue inside our heads that makes us see the world, have feelings, make decisions.” By creating the “connectome,” a comprehensive wiring diagram of the brain, researchers are not merely mapping structure but also merging it with functional insights—something that previously eluded them. The ability to visualize how neurons communicate and integrate their signals opens the doors to a nuanced understanding of the cerebral ballet that dictates our existence.
Technological Triumphs and New Possibilities
The experimental design was as cerebral as the output—mice were shown clips from iconic films like “The Matrix” while running on a treadmill, allowing researchers to monitor brain activity under different stimuli. Dissecting the brain into 28,000 layers provided the perfect milieu for analysis. This duality of structure and function has been highlighted by Princeton’s H. Sebastian Seung, who states, “The connectome is the beginning of the digital transformation of brain science.” Such a statement holds more than mere optimism; it embodies a future where our comprehension of cognitive processes could mirror the progression seen in technology.
Making this data publicly available represents a significant shift in scientific culture; it allows for an open-source approach to neuroscience, enabling other researchers to build upon these findings. This collaborative spirit could ignite innovations in artificial intelligence, propelling AI systems towards more adaptable, brain-like processing. Human cognition has, until now, eclipsed the capabilities of even the most advanced algorithms, and understanding its intricacies will only serve to deepen that chasm or skillfully bridge it.
Implications for Mental Health and Disease
The ramifications of this research are impressive, particularly in relation to mental health. Diseases like dementia and other neurological disorders could find new avenues of treatment grounded in the details unearthed by the connectome. Understanding the “normal” wiring of the brain can establish a baseline from which deviations can be identified. This is not just theoretical; Seung emphasizes the real possibility of identifying abnormal connectivity patterns that may lead to disorders, which could revolutionize how clinicians diagnose and treat patients.
Moreover, this venture into the depths of brain architecture serves as a mirror reflecting the complexities of the human condition. As we uncover the mechanisms behind every thought, emotion, and decision made in our cerebral universe, we inch closer to addressing mental health crises that plague modern society. Researchers are now armed with the tools to explore potential therapies, interventions, and preventive measures that can significantly alter the quality of life for those affected by debilitating conditions.
In a world where the fog of misconception often clouds our understanding of the mind, it’s imperative that we embrace these scientific revelations. They not only expand our knowledge base but also frame a future where the impossible becomes attainable, effectively bridging the gap between humanity and the machinery of our thoughts.
Leave a Reply